-
Date:
10 Apr 2025
-
Location:
Room 2.2.14 - Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon & Online
-
Schedule:
12h00 (Lisbon time)
-
Lecturer or Responsible:
Pedro Gameiro dos Santos (CE3C-EMDD)
Important Notice
We sincerely apologise, but we were unable to establish a Zoom connection due to unexpected internet issues. We regret any inconvenience this may have caused and appreciate your understanding.
Thank you for your patience.
Online access • LINK
Password • scientia
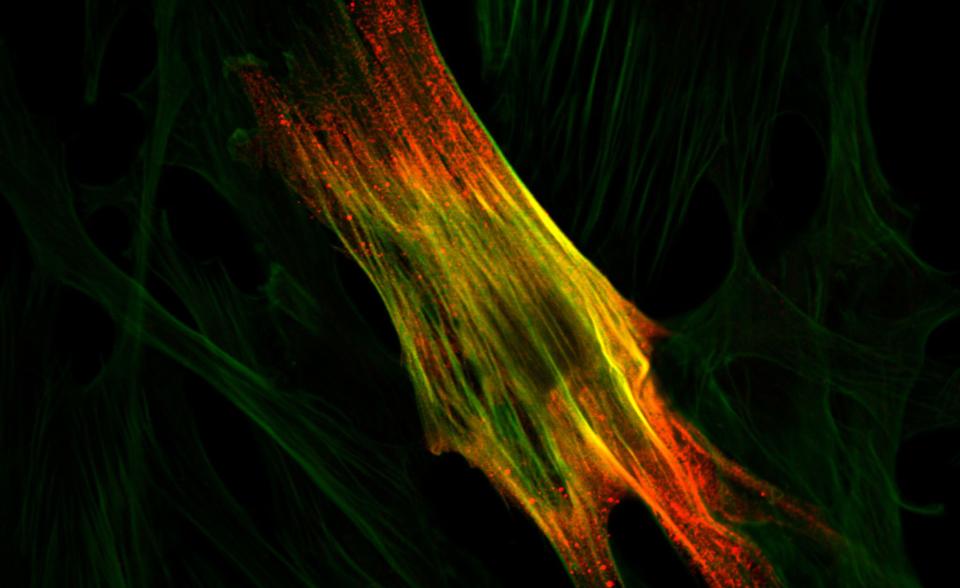
Laminin-211 is a key extracellular matrix protein essential for skeletal muscle integrity. Its absence in LAMA2-congenital muscular dystrophy (LAMA2-CMD) leads to severe muscle degeneration. To investigate underlying mechanisms, we analyzed myoblast differentiation in C2C12 cells, dyW mouse primary myoblasts, and human patient-derived myoblasts. Lama2-deficient (KO) C2C12 cells exhibited severe differentiation defects, forming sparse, underdeveloped myotubes and showing reduced Myosin Heavy Chain (MyHC) expression. Similar impairments were observed in dyW myoblasts, with reduced myotube formation after three days. KO C2C12 cells showed downregulation of Myog, Myl1, Tubb6, reduced MYF5-positive nuclei, and increased NFIX, a marker of aberrant fetal myogenesis. In human patient-derived cells, we observed deregulation of myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs), reduced MYOG-positive nuclei and downregulation of differentiation-related genes. These conserved defects across species underscore the translational relevance of patient-derived models in understanding LAMA2-CMD and reinforce their value in bridging the gap between animal studies and clinical application.

